MODULE 3: MAGNETOSTATICS
BIO-SAVART LAW, DIVERGENCE AND CURL OF STATIC MAGNETIC FIELD; VECTOR POTENTIAL AND CALCULATING IT FOR A GIVEN MAGNETIC FIELD USING STOKES’ THEOREM; THE EQUATION FOR THE VECTOR POTENTIAL AND ITS SOLUTION FOR GIVEN CURRENT DENSITIES.
Biot-Savart
law
The Biot-Savart law describes the magnetic field produced by a steady current flowing in a conductor. The law mathematically expresses the magnetic field contribution (dB) at a point in space due to an infinitesimally small current element (Idl).
Biot-Savart law named after the French physicists Jean-Baptiste Biot and Félix Savart
steady current = constant current
current element = the product of current and infinitesimal conductor length
Statement
Biot-savart law states that the magnetic field due to a current carrying conductor at a distance r is inversely proportional to the square of the distance r, and the magnetic field is directly proportional to the product of current element (Idl) and sine of angle q between current element and distance r.
According to Biot-Savart law
Question 01
For a straight current-carrying wire, how does the magnitude of the magnetic field vary with the distance from the wire according to the Biot-Savart law?
A. Linearly increases with distance
B. Quadratically increases with distance
C. Inversely proportional to the square of the distance
D. Inversely proportional to the distance
Answer: D. Inversely proportional to the distance
Question 02
What does the Biot-Savart law describe in electromagnetism?
A. Electric field generated by a stationary charge
B. Magnetic field produced by a steady current
C. Relationship between voltage and current in a circuit
D. Electrostatic forces between charged particles
Answer: B. Magnetic field produced by a steady current
Question 03
In the Biot-Savart law, what does Idl represent?
A. Electric current in the conductor
B. Infinitesimal current element
C. Permeability of free space
D. Distance between two current-carrying wires
Answer: B. Infinitesimal current element
Question 04
What physical quantity does the permeability of free space μ0 represent in the Biot-Savart law?
A. Electric charge
B. Electric field
C. Magnetic permeability
D. Permittivity
Answer: C. Magnetic permeability
Question 05
In the Biot-Savart law, what happens to the magnetic field as the distance from the current element increases?
A. It remains constant.
B. It decreases inversely with distance.
C. It increases linearly with distance.
D. It varies depending on the direction of the current.
Answer: B. It decreases inversely with distance.
Question 06
Which of the following equations represents the Biot-Savart law in integral form?
Answer: B
Question 07
What does the Biot-Savart law primarily deal with in terms of current characteristics?
A. Time-varying currents
B. Non-steady currents
C. Steady currents
D. Alternating currents
Answer: C. Steady currents
Question 08
For a straight current-carrying wire, how does the magnitude of the magnetic field vary with the distance from the wire according to the Biot-Savart law?
A. Linearly increases with distance
B. Quadratically increases with distance
C. Inversely proportional to the square of the distance
D. Inversely proportional to the distance
Answer: D. Inversely proportional to the distance

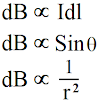


No comments:
Post a Comment