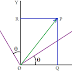
Transformation of Scalars and Vectors under Rotation Transformation
Q.1. Explain “Transformation of Scalars under Rotation Transformation” .
Q.2. Explain “Transformation of Vectors under Rotation Transformation” .
Q.3. Explain “Transformation of Scalars and Vectors under Rotation Transformation” .
Q.4. If a vector of magnitude A is rotated through certain degree, then what is the change in that
vector?
forces in nature
Q.5. Explain forces in nature.
Q.6. Explain about the basic forces in nature with its range and magnitude.
Form Invariance of Newton’s Second Law
Q.7. What do you mean by form Invariance of Newton’s second law, Explain.
Q.8. Define Galelian Transformations. Derive the Transformation Equations.
Friction
Q.9.Define the term friction ? Explain types of friction.
Q.10. write the differences between static friction and dynamic friction.
Q.11. State the laws of friction.
Q.12. Explain the term angle of friction.
Q.13. Define coefficient of friction and limiting friction.
Newton’s equations of motion in Cartesian Coordinates
Q.14. The position of a particle of mass m under the influence of a free particle is given by
Find the expression for its momentum. (AKU 2020)
Q.14.The transformation
matrix to move from a set of coordinates axes to a new set x¢, y¢, z¢
through
an angle q is
Q.15. If a position
vector ![]() is represented in a set of x,y,z
co-ordinate
is represented in a set of x,y,z
co-ordinate
transformed value of the components of the position vector A in new co-ordinate
system of x¢, y¢,z¢.